How you can protect yourself?

Secure Banking
Secure your computer
- Always use a trusted computer and avoid using a shared or public computer for banking.
- Ensure your computer is equipped with antivirus and firewall to prevent any malware infection.
- Update your computer regularly , especially the antivirus software, web browser and operating system
Do not miss important banking signposts designed to provide you information to detect a fraud
- Type in the bank's website address to browse the banks web page.
- Do not use your banking password for anything else, such as your email account.
- Pay attention to last logged in date and time
- Periodically review your beneficiaries to ensure only beneficiaries added by you are present at your account
Be careful while travelling
- Consider enabling roaming when out of country so that you do not miss important notifications from RAKBANK
- Do not use unsecure Wi-Fi access points such as the ones present at airports
Common Fraud Scenarios - Phishing
Phishing is the attempt to acquire sensitive information such as usernames, passwords, and credit card details (and sometimes, indirectly, money), often for malicious reasons, by masquerading as a trustworthy entity in an electronic communication.
- Look for a secure connection. This is usually identified by a green area in the address bar, along with https in the URL.
- Look at the domain of the URL. If you don’t know what the domain of a URL is, here is an example: The domain of RAKBANK is rakbank.ae, while the domain of RAKBANKOnline is rakbankonline.ae, and so on. Look to see that the domain is as it should be, and not something bizarre with spelling errors.
- Look at the site itself. If it doesn’t look exactly like the site you’re always used to, it may be a scam site. You can double check by opening a new tab and visiting the main page of the site you think you’re on (if possible). If they’re quite different, then you’re more than likely dealing with a phishing site.
Common Fraud Scenarios - Vishing
Vishing is the act of using the telephone in an attempt to scam the user into surrendering private information that will be used for identity theft. The scammer usually pretends to be a legitimate business, and fools the victim into thinking he or she will profit.
- As a rule of thumb, don’t give out any information over the phone if you’re unsure of who’s calling. If you have any doubts at all, hang up. Credit cards, bills and bank statements should all feature customer service numbers that you can use to see if the call you just received was legitimate.
Common Fraud Scenarios - SMShing
SMShing is the mobile phone version of phishing. An example of SMShing fraud would be a text message that appears to be sent from a legitimate source, such as a bank or credit card company, that urgently requests the recipient to call a phone number or follow a link in the message. The phone number or website will then ask for sensitive account or personal information.
- Never take action on a request for your personal or financial information, including account numbers, passwords, Social Security number or birth date. If you receive a text message expressing an urgent need for you to update your information, activate an account, or verify your identity by calling a phone number or submitting information, on a website, do not respond and delete it. These messages may be part of a phishing scam conducted by fraudsters in an attempt to capture your confidential account information and may be used to commit fraud.
Common Fraud Scenarios - Malware and Ransomware
Malware is an umbrella term used to refer to a variety of forms of hostile or intrusive software, including computer viruses, worms, trojan horses, ransomware, spyware, adware, scareware, and other malicious programs.
Ransomware is a security threat that has data-kidnapping capabilities. Ransomware is a malicious software that denies you access to your computer or files until you pay a ransom.
- Ensure anti-virus software is updated on both your office PC and home PC
- Bookmark websites to ensure you do not accidentally mistype an incorrect address, do not trust links sent over SMS, instant messaging and email from unknown sources.
- Be wary of free screensavers, games, browser add-ons, peer-to-peer (P2P) clients, and any downloads claiming to be cracked or free versions of expensive applications, such as Adobe, PhotoShop or Microsoft Office.
Common Fraud Scenarios - E-mail Spoofing
E-mail Spoofing is the forgery of an e-mail header so that the message appears to have originated from someone or somewhere other than the actual source. Distributors of spam often use spoofing in an attempt to get recipients to open, and possibly even respond to, their solicitations. Spoofing can be used legitimately.
- Always look for the content of the email. Spoofed emails are tend to look like sent from legitimate source. However you will be able to determine if it’s a spoofed email if the email seems to asking you for confidential information like user name, password, bank account number etc. details.
- Or even at times the email may even look like from legitimate source and has some kind of an attachment or link to a website which can further ask you to furnish confidential information.
- If in doubt please contact our contact center and have it confirmed with a call center agent.
Common Fraud Scenarios - Shoulder surfing
Shoulder surfing, in computer security refers to using direct observation techniques, such as looking over someone's shoulder, to get information. It is commonly used to obtain passwords, PINs, security codes, and similar data.
- When working on a laptop, ensure that your back is to a wall with no open sides close to you or to enter your passwords in a secluded location
- When keying in PIN at ATM make sure no on in standing right behind you.
How to recognize a genuine RAKBANK website
You can check whether you're currently on RAKBANK's genuine site or visiting a Phishing website by following the steps below:
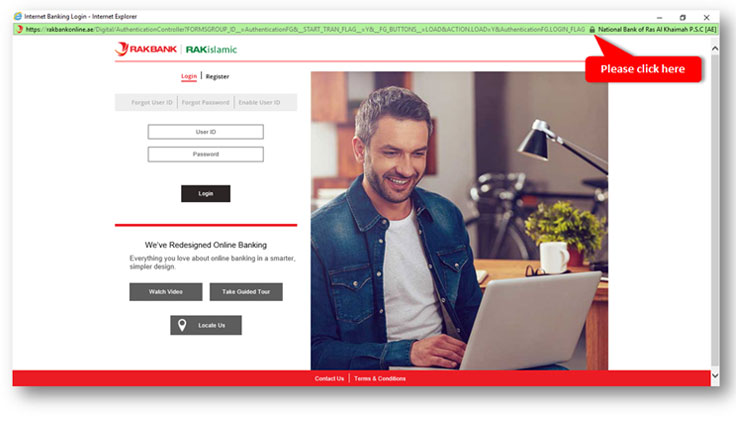
Step 1 Click on the Padlock in your browser window (shown in the image below)
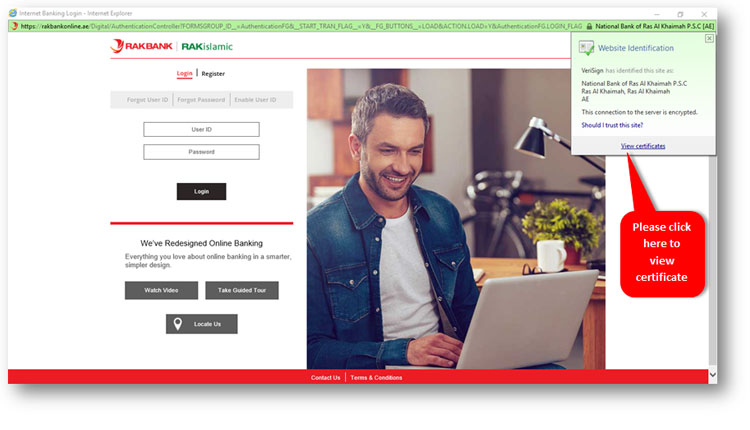
Step 2 Click on the View Certificate link to view the original certificate information (shown in the image below)
Step 3 Verify that SSL certificate issued to RAKBANK is a valid certificate it has an expiry date and issued by Certificate Authority – Symantec (shown in the image below)

What to do if you suspect your account has been compromised?
If you have any suspicions at all, please stop using the website immediately and contact the RAKBANK Call Centre (+9714 213 0000) for assistance. They will be able to guide you through any security checks that you may need to perform and tell you when it is safe for you to continue.


 Apple Pay
Apple Pay

